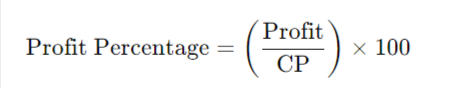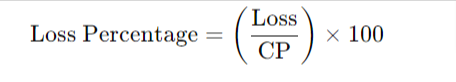When dealing with the buying and selling of goods, it's essential to understand some fundamental concepts that help determine profitability. These include Cost Price (CP), Selling Price (SP), Profit, Loss, Marked Price (MP), Discount, and their respective percentages. Let's delve into these concepts and see how they apply in practical scenarios through examples.
Key Concepts
-
Cost Price (CP):
- The cost price is the amount at which a product or service is purchased. This includes the cost of production, manufacturing, or acquisition of the product.
-
Selling Price (SP):
- The selling price is the amount at which a product or service is sold to customers.
-
Profit (P):
- Profit is the amount earned when the selling price is higher than the cost price. It is calculated as: Profit=SP−CP\text{Profit} = \text{SP} - \text{CP}
-
Loss (L):
- Loss is the deficit incurred when the selling price is lower than the cost price. It is calculated as: Loss=CP−SP\text{Loss} = \text{CP} - \text{SP}
-
Marked Price (MP):
- The marked price is the original price of a product or service as indicated on the price tag or label.
-
Discount (D):
- A discount is a reduction in the marked price of a product or service, usually offered to attract customers or clear old stock.
-
Profit Percentage (P%):
-
Loss Percentage (L%):
Practical Examples
Example 1: A shopkeeper bought a toy for Rs. 500 and sold it for Rs. 650. What is the profit percentage?
- Solution:
- CP = Rs. 500
- SP = Rs. 650
- Profit = SP - CP = Rs. 650 - Rs. 500 = Rs. 150
- Profit Percentage = (150500)×100=30%\left(\frac{150}{500}\right) \times 100 = 30\%
- Answer: 30%
Example 2: A shirt was bought for Rs. 800 and sold at a loss of 12.5%. What was the selling price?
- Solution:
- CP = Rs. 800
- Loss Percentage = 12.5%
- Loss = 12.5% of CP = 0.125 × Rs. 800 = Rs. 100
- SP = CP - Loss = Rs. 800 - Rs. 100 = Rs. 700
- Answer: Rs. 700
Example 3: A trader sold a mobile phone for Rs. 9,000 and incurred a loss of 10%. What was the cost price of the mobile phone?
- Solution:
- SP = Rs. 9,000
- Loss Percentage = 10%
- Loss = 10% of CP
- SP = CP - Loss = CP - 0.10 × CP = 0.90 × CP
- CP = SP / 0.90 = Rs. 9,000 / 0.90 = Rs. 10,000
- Answer: Rs. 10,000
Example 4: If the cost price of an item is Rs. 200 and it is sold at a profit of 20%, what is the selling price?
- Solution:
- CP = Rs. 200
- Profit Percentage = 20%
- Profit = 20% of CP = 0.20 × Rs. 200 = Rs. 40
- SP = CP + Profit = Rs. 200 + Rs. 40 = Rs. 240
- Answer: Rs. 240
Example 5: A shopkeeper offers a discount of 20% on a pair of shoes. If the marked price is Rs. 1,500, what is the selling price after the discount?
- Solution:
- MP = Rs. 1,500
- Discount = 20% of MP = 0.20 × Rs. 1,500 = Rs. 300
- SP = MP - Discount = Rs. 1,500 - Rs. 300 = Rs. 1,200
- Answer: Rs. 1,200
Example 6: A trader bought 15 pens for Rs. 750 and sold them at a profit of 30%. What was the selling price of each pen?
- Solution:
- Total CP for 15 pens = Rs. 750
- CP per pen = Rs. 750 / 15 = Rs. 50
- Profit Percentage = 30%
- Profit per pen = 30% of CP per pen = 0.30 × Rs. 50 = Rs. 15
- SP per pen = CP per pen + Profit per pen = Rs. 50 + Rs. 15 = Rs. 65
- Answer: Rs. 65
Example 7: A shirt was sold for Rs. 800 at a loss of 20%. What was the cost price of the shirt?
- Solution:
- SP = Rs. 800
- Loss Percentage = 20%
- Loss = 20% of CP
- SP = CP - Loss = CP - 0.20 × CP = 0.80 × CP
- CP = SP / 0.80 = Rs. 800 / 0.80 = Rs. 1,000
- Answer: Rs. 1,000
Example 8: A toy was bought for Rs. 200 and sold for Rs. 250. What was the percentage of profit?
- Solution:
- CP = Rs. 200
- SP = Rs. 250
- Profit = SP - CP = Rs. 250 - Rs. 200 = Rs. 50
- Profit Percentage = (50200)×100=25%\left(\frac{50}{200}\right) \times 100 = 25\%
- Answer: 25%
Example 9: A trader sold a TV for Rs. 12,000 at a profit of 25%. What was the cost price of the TV?
- Solution:
- SP = Rs. 12,000
- Profit Percentage = 25%
- Profit = 25% of CP
- SP = CP + Profit = CP + 0.25 × CP = 1.25 × CP
- CP = SP / 1.25 = Rs. 12,000 / 1.25 = Rs. 9,600
- Answer: Rs. 9,600
Example 10: A book was sold at a loss of 8%. If the selling price was Rs. 460, what was the cost price?
- Solution:
- SP = Rs. 460
- Loss Percentage = 8%
- Loss = 8% of CP
- SP = CP - Loss = CP - 0.08 × CP = 0.92 × CP
- CP = SP / 0.92 = Rs. 460 / 0.92 = Rs. 500
- Answer: Rs. 500
Multiple-Choice Questions (MCQs)
-
A shopkeeper bought a toy for Rs. 500 and sold it for Rs. 650. What is the profit percentage?
- a) 15%
- b) 20%
- c) 25%
- d) 30%
- Answer: c) 25%
-
A shirt was bought for Rs. 800 and sold at a loss of 12.5%. What was the selling price?
- a) Rs. 680
- b) Rs. 700
- c) Rs. 720
- d) Rs. 750
- Answer: c) Rs. 720
-
A trader sold a mobile phone for Rs. 9,000 and incurred a loss of 10%. What was the cost price of the mobile phone?
- a) Rs. 9,500
- b) Rs. 10,000
- c) Rs. 10,500
- d) Rs. 11,000
- Answer: d) Rs. 11,000
-
If the cost price of an item is Rs. 200 and it is sold at a profit of 20%, what is the selling price?
- a) Rs. 220
- b) Rs. 240
- c) Rs. 250
- d) Rs. 260